Subtract the amount by which you need to replenish the account from the total amount of your vouchers. A negative result represents a cash short amount, while a positive number represents a cash over amount. The custodian should prepare a voucher for each disbursement and staple any source documents (invoices, receipts, etc.) for expenditures to the petty cash voucher. At all times, the employee responsible for petty cash is accountable for having cash and petty cash vouchers equal to the total amount of the fund. After the check is cashed, the petty cash custodian normally places the money in a small box that can be locked.
Real-World Example of Cash and Cash Equivalents
The cash over and short account is used to record the difference between the expected cash balance and the actual cash balance in the imprest account. A firm should note instances of cash variances in a single, easily accessible account. The opposite is true about transactions that produce cash shortages. Assume the same situation except Tom only receives $99 instead of $101.

Assets vs. Liabilities
Then, when the benefits of these assets are realized over time, the amount is then recorded as an expense. Some assets are recorded on companies’ balance sheets using the concept of historical cost. It represents the original cost is cash short and over an asset of the asset when purchased by the company and can also include expenses (such as delivery and set up) incurred to incorporate an asset into the company’s operations. Current assets are typically liquid, meaning they can be quickly converted into cash.
Examples of expenses vs. liabilities
However, every company and industry will have different cash requirements, thus, there will always be different values that are considered good. To record the cash shortfall the business needs to enter the cash shortage of 12 as part of the journal entry used to record the sales as follows. Cash shortages are recorded in https://x.com/BooksTimeInc a separate income statement expense account usually known as the cash short or over account. Savings and checking accounts (cash) and money market accounts (cash equivalents) are often insured up to $250,000 by the FDIC.

Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
- Alternatively, credit your cash short and over account by the amount of cash over.
- You need to know what your cash ratio looks like in relation to your liquidity ratios.
- In the example, debit your cash short and over account by $10 to record the cash short amount.
- Some assets are recorded on companies’ balance sheets using the concept of historical cost.
- A bet on the over means you think both teams will combine to score more goals, points, or runs than the total listed.
- Current assets are those assets that can be converted into cash within one year.
Current assets are referred to as current because they are either cash or can be converted into cash within one year. The assets included in this metric are known as “quick” assets because they can be converted quickly into cash. Prepaid expenses are advance payments made for goods or services to be received in the future. This includes products sold for cash and resources consumed during regular https://www.bookstime.com/articles/schedule-k-1 business operations that are expected to deliver a cash return within a year. Current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash within a period of one year. Examples of liabilities include loans, tax obligations, and accounts payable.
Cash and Cash Equivalents (CCE): Definition, Types, and Examples
In these cases, cash variances should be stored in a single, easily-accessible account. For this reason, companies typically establish a petty cash fund that needs to be replenished every two to four weeks. Shorting is a strategy used when an investor anticipates the price of a security will fall in the short term. There are some exceptions to short-term assets and current assets being classified as cash and cash equivalents.
Quick Ratio
- Here are some of the use cases you may run into when understanding the uses of assets and liabilities.
- If a company has a cash short situation, which is more common, the amount it is short will reduce the company’s net income and its cash balance in the general ledger.
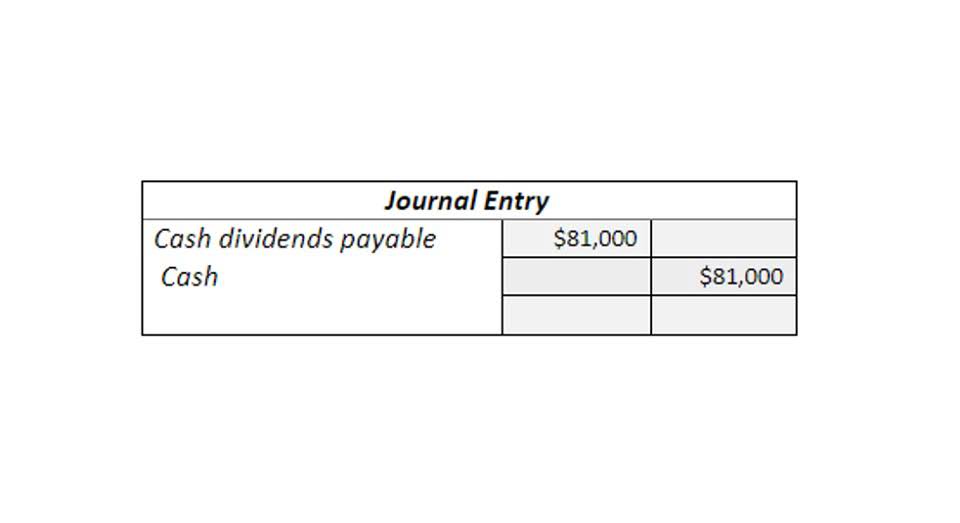
- Credit, or decrease, your cash account by the amount by which you must replenish the petty cash account in the journal entry.
- Cash equivalents are short-term investments that can be easily liquidated, carry low risk of loss, and have active marketplaces to ensure quick transacting.
- This category includes any other asset that can be quickly converted into cash.
- If Julia had a cash over situation instead, it would increase the company’s net income and add to the cash balance in the petty cash fund.
Any discrepancy should be debited or credited to an account called Cash Over and Short. The Cash Over and Short account can be either an expense (short) or a revenue (over), depending on whether it has a debit or credit balance. Working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities. It represents a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations.
Those can be financial assets like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, or physical assets like a home or an art collection. In most cases, customers will most likely to dispute a shortage of change. Therefore, the cash over and short is usually at debit balance which represents an expense.
What Is an Asset? Definition, Types, and Examples
Cash equivalents include all assets that can quickly be turned into cash. These include treasury bills, bank certificates of deposit, commercial paper, and other money market instruments. A cash shortage normally occurs in a retail environment when the sales are reconciled to the cash receipts in the register at the end of the trading day. If the cash in the register is less than the sales there is said to be a cash shortage. Likewise, if the cash is greater than the sales the cash is said to be over. In contrast, let’s assume that during the cash count, the actual cash from the cash sales is $495 instead of $510.
